How to draw a budget for a project
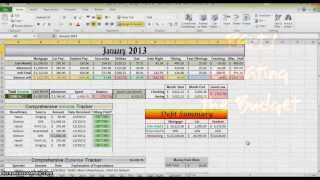
Pages: find an and cost accounting costs other than ties & administrative recovery of f&a costs - calculating ipant support es in sponsored ntly required the university of al writer's ic program zing your writing e foundation ch proposals - abstract or ch proposals - ch proposals - background or ch proposals - ch proposals - ch proposals - cover ch proposals - institutional ch proposals - plan or ch proposals - project ch proposals - ch proposals - table of proposals are sharing pal investigator rds, hybrid agreements and purchase are herehomedevelop proposalproposal writer's guideresearch proposals - parts of a ound or utional ic program e foundation zing your writing proposals are budget section: budget & budget budget is a line item (tabular) representation of the expenses associated with the proposal project. The budget justification contains more in depth detail of the costs behind the line items, and sometimes explains the use of the funds where not evident. The need to travel to professional meetings should be tied to the proposed project, if possible. Refer to sample estimates need to be as accurate as possible to cover the expenses proposed in the project. Reviewers will note both over- and budget should be developed with your departmental research administrator, in consultation with the appropriate orsp project representative as needed. The overview given here is for preliminary guidance l divisions of the line item (tabular) budget are personnel, equipment, supplies, services, travel, and indirect costs (idc). The budget should make clear how the totals for each category of expenses are reached. Category of personnel includes not only the base salary or wage for each person on the project, but also (listed separately) the percentage added for staff benefits. Project representatives should be consulted on the calculation of staff benefits, because the rate may vary significantly depending on the kinds of personnel involved and the selected benefit option. A table is available from te student research assistants, who are to be employed on research projects for more than 1/2 time, may have part of their tuition costs covered by their unit.

How to draw up a budget for a project
The remaining tuition costs must be included as a line item in the budget to the ct costs (idc) are shown as a separate category, usually as the last item before the grand total. Equipment (over $5,000), graduate research assistant tuition, and the balance of subcontracts over $25,e indirect cost percentages change after periodic negotiations with the federal government, pis should consult their departmental research administrator or an orsp project representative before calculating this part of their budget. Refer here for the current indirect cost (idc) cost sharing is required (mandated) by the sponsor, please check with your departmental research administrator for how to show that in the budget. This must be approved by your chair or call attention to the variety of expenses that might arise in the conduct of a research project, a checklist* of possible budget items is included here. This checklist suggests many of the expenses that might be appropriate to your budget, but consultation with the orsp project representative is important. S/he can help ensure (1) that the budget has not omitted appropriate elements of cost, such as service charges for the use of certain university facilities (for example, surveys conducted by the institute for social research); (2) that any estimates for construction, alterations, or equipment installation have been properly obtained and recorded; (3) that costs are not duplicated between the direct and indirect cost categories; (4) that the budget complies with any cost-sharing requirements of the sponsor; (5) that provisions are made for the escalation of costs as may be appropriate; and (6) that costs in all categories are realistically additional help and samples, see budget planning & ist for proposal budget items directly tied to the project:A. Proposal prep and unit review - 11/15/ instructor-led, hands-on training session covers the process of preparing and submitting proposals using the eresearch proposal management (erpm) system, including er 15, 2017 1:00 proposal prep and unit review - 12/13/er for instructor-led, hands-on training session covers the process of preparing and submitting proposals using er 13, 2017 1:00 on: thursday, january 7, 2016 - 12: hub project mentchange oktwittergoogle+ others are ment matrix template for project milestone templates for oft office life cycle project software reviews & by @brighthub_ for emailsclick here to signup for our newsletter ». Updated: 4/22/2012success in project management hinges on the creation of a comprehensive and accurate project budget. Find out what to include in your budget and download a free example of a project budget is the goal of a project budget? It is a pivotal tool that will be used by several different groups involved in the project.

The project manager will use this budget to determine whether the project is on track; project personnel will use it as a guideline to fulfill certain project milestones; and the client will use it to determine the success of the the task of creating a budget for a new project may be a bit daunting- especially if the project manager has had little or no experience coordinating projects. But there are many contingencies and unknowns that may affect how and when the project is carried out and ultimately completed. The most important point to keep in mind is that although a project budget should be based on concrete numbers and accurate assessments of the resources needed to complete the task, the bottom line is that a budget is meant to be an should you include in your project budget? Detailed, line-item budget should be divided into categories such as salaries, fringe benefits, travel, supplies, and equipment. Make sure to also include any overhead costs (called "indirect costs") that will be associated with the project. Here is a brief description of some of the major expenses you will need to include:Employee compensation: this section includes the salaries and wages of all full, part-time, and temporary employees involved in the project. You should also include any other benefits and incentives that may not be reflected in their take home ct services: here you should include outsourced services or workers, such as ent/supplies: this section covers expenses for office supplies, postage, copier supplies, telephone, fax, computer supplies, equipment repair and maintenance, laboratory consumables, /related expenses: make sure that you include any air travel, out of town expenses, conference travel expenses as well as daily parking and mileage ad or indirect costs: your budge should also include overhead expenses (indirect costs), which allow the project to bear a portion of the administrative costs of the day-to-day example of project management following is an example of the typical expenses included in a project budget. To assist you in your budgeting efforts, this sample budget can also be downloaded as a template in excel for a year-long project. Prolect expenses: employee compensation:Salary bonus & commissions employee incentive employee benefits temporary salary & benefits other expenses:Seminars & training consulting fees legal fees other professional fees contracted services recruitment advertising marketing materials travel & entertainment office expense telephone computer lease repairs & maintenance utilities office supplies dues & subscriptions office rent postage general insurance taxes & licenses software other expenses total budgeted enable javascript to view the comments powered by disqus. Prolect expenses: employee compensation:Salary bonus & commissions employee incentive employee benefits temporary salary & benefits other expenses:Seminars & training consulting fees legal fees other professional fees contracted services recruitment advertising marketing materials travel & entertainment office expense telephone computer lease repairs & maintenance utilities office supplies dues & subscriptions office rent postage general insurance taxes & licenses software other expenses total budgeted enable javascript to view the comments powered by images / getty d june 19, enced project managers and those who work in big companies will have software and accountants to help them put together project budgets.

If you are staring at a blank spreadsheet or an email from your project sponsor asking you to put together the finances for the project, then this article is for ’ll look at the five things you need to do in order to create a basic project your task listfirst, take your project task list. Write down everything that you have to do and the things you have to build or make or complete before the project can be finished. It doesn’t have to be in any particular order, but it does need to include y on this step, brainstorm ideas with your project team, as there is bound to be something you have forgotten. For example, a task that says ‘set up meetings to discuss requirements’ might involve sourcing and hiring the meeting rooms or buying any resources you need like a projector or flip chart is a cost involved with that, so get quotes for your room hire and the other equipment and note it this for everything on the task list so you end up with a price against every item. Some project tasks may not have a price attached and that’s estimates togethernext add together all your ’s easiest to do this if you make a list of items in a spreadsheet, add the costs in the next column and then total the column at the bottom. This becomes your budget is a good idea to group your costs into categories as well, so you can easily see where the bulk of the money is going. Use categories like ‘project start up’, ‘infrastructure’ or ‘training’ – choose groupings that mean something in the context of the contingency and taxesit would be great if you had a crystal ball and could predict these costs with 100% accuracy but you probably don’t feel confident in your ability to do that! This is a non-scientific guesstimate that many project managers use and gives you a little bit of cushioning in your budget in case you need a line on your budget spreadsheet at the bottom that says ‘contingency’ and specifies the percentage you ’t forget to add in any sales tax or other taxes that are not explicitly already included in your individual line item it all up and that’s your final budget approvalthe final thing to do is to get your manager or project sponsor to approve your budget. Project budgeting is a basic project management skill and this guide will get you started creating a project is the role and purpose of a project charter? You can do to capitalize on positive to include in your project risk t governance 101: everything you need to to manage your project without a gantt chart.
Project boards do and why it complete guide to increasing your project management how you can benefit from a project audit. Habits of successful project what a project milestone is and how it's used to track a ng changes on projects while keeping it moving is project time management? More than that, you need to show how spending that money will help you to answer your research , developing the budget is the perfect time to plan your project clearly. A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project. List your a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is going to do your methodology and turn it into a step-by-step plan. You need to go to kuala lumpur to interview x number of people over y weeks, then the same again for singapore and budget list might look like this:I’m going to do 10 interviews in kuala lumpur; 10 interviews in singapore; 10 interviews in jakarta by me. Ll do the writing up in my research allowance the end, you should feel like you have thought through the entire project in detail. You should be able to walk someone else through the project, so grab a critical friend and read the list to them. If not, go and read them now – i’ll wait right here until you get you’ve listed everything you want to do, go back and read the specific rules for budgets again. It is just as important to know what you can include in the application that you are writing right funding schemes won’t fund infrastructure (like building costs) and other things that aren’t directly related to the project.
Once again, your finance officer can help with budget list might now look like this:10 interviews in kuala lumpur; 10 interviews in singapore; 10 interviews in jakarta by ng release for three months for s to kl, singapore, jakarta and back to odation for a month in each place, plus per diem, plus travel insurance (rule 3f). Organise access to thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project. You are going to be doing research budgets for the rest of your research you are working with budgets, a spreadsheet is the right tool for the job, so learn to use it! Learn enough to construct a simple budget – adding things up and multiplying things together will get you through most of it. Per day, and it will also add up all of your sub-totals for your budget doesn’t add up properly (because, for example, you constructed it as a table in word), two things will happen. If your total is wrong, they will start to question the validity of the rest of your budget. For each item in your budget, you need to answer two questions:Why do you need this money? Everything item in your budget should be listed in your budget justification, so take the list from your budget and paste it into your budget each item, give a short paragraph that says why you need it. Is an example for just one aspect of the budget:Fieldwork: kuala experience has shown that one month allows enough time to refine and localise interview questions with research partners at university of malaya, test interview instrument, recruit participants, conduct ten x one-hour interviews with field notes. If you list a thingatron x32c in your budget, then call it a thingatron x32c in your budget justification and project plan.

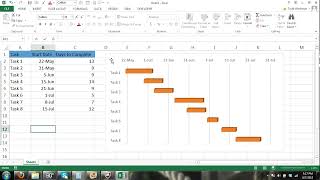
In an ideal world, someone should be able to flip from the project plan, to the budget and to the budget justification and back again and always know exactly where they t plan: “doing fieldwork in malaysia? Flips to budget justification: “ah, the field work happens at the same time as the conference. Jonathan o’ not to pad your budget – tseen r the budget, conquer the project – tseen ch on a shoestring – emily to make a simple gantt chart – jonathan o’donnell. However, you will still need to work out what you are going to spend the money on, so you will still need a budget at some stage, even if you don’t need it for the in the ‘simple grant’ series:How to write a simple research methods to make a simple gantt this:facebooktwitterlinkedinpocketemailprintlike this:like loading... Under apply for funding, top with budget, jonathan o'donnelljonathan o'donnell helps people get funding for their research. Humorous way to talk explain a serious subject and could be helpful in designing budgets for outreach grants, as well. O'donnell says:6 january 2015 at 8:09 you are interested, i have another one on how to do a timeline:Pingback: the research project budget! Friend of mine recently commented by e-mail:I was interested in your blog “how to make a simple research budget”, particularly the statement: “think through the implications of what you are going to do. How to start a research collaboration | piirus ck: pitfall 2: leaving the budget till last | ck: how to make a simple research budget | oars research ck: “research whisperer” explains how to build a simple research budget | oars research news. You or your organisation is preparing a proposal to apply for funds to carry out a project, there are a number of sections you will have to complete.

However, what you do or do not include in the budget section of your application could be the difference between success and failure. In the following lines, you will find the principles of developing a budget, including the type of costs and how to calculate them. Furthermore, you will find tips on how to prepare a successful, honest and well-balanced budget, in line with the activities set in your project proposal. Budget is defined as patterns of expenditure and revenue over the life of the project (seaga 2001). In general, it is a prediction of the possible costs that will be incurred by carrying out the activities planned in a project. A professional and transparent approach to budget planning will help convince investors, development banks and national or international donors to make financial resources available (philip et al. All different tasks when allocating the budget can be a challenge… source: wsp (2004)generally, the budget has mainly two functions. First, it estimates, as realistically as possible, the cost of completing the objectives identified in the project proposal. The sponsoring agencies will use the budget details to determine whether the proposal is economically feasible and realistic. Secondly, the budget provides a means to monitor the project's financial activities over the life of the project.

In this way, it is possible to determine how closely the actual progress toward achieving the objectives is being made relative to the proposed budget (university of virginia 2010). Sponsors, especially government agencies and international organisations, provide either a form or a format for the budget. In fact, the first thing you should do is read the application guidelines carefully so you are sure of what you need to include — or exclude — in your case there is not a specific guideline for the development of your budget, the following section will help you to prepare a realistic and well-balanced to start? Drawing up the budget, it is necessary to get an overview of the type of inputs needed to achieve the objectives of the project. As the budget should be in line with the activities set in the work plan, you should work through the narrative of the proposal identifying all the costs that must be incurred in order to carry out each single activity planned. Further budget developmentonce you have identified the type of expenditures your project will have, the next step is to classify them according to standard budget categories. Budget’s items are generally divided into two classifications: direct costs and indirect ing to the european commission (ec 2009) “direct costs are all those eligible costs which can be attributed directly to the project and are identified by the beneficiary as such, in accordance with its accounting principles and its usual internal rules”. You will need to consider the costs of renting or maintaining a car for the purposes of the project. Funding agencies have different views on the purchase and maintenance of equipment, so be sure you know the policy of the agency before including such costs in your budget (university of idaho 2010). Indirect costs are all those eligible costs which cannot be identified by the beneficiary as being directly attributed to the project, but which can be identified and justified by its accounting system as being incurred in direct relationship with the eligible direct costs attributed to the project (ec 2009).

Rules for determining the overhead in a funding programme is usually given by the donor, so be sure to find out what percentage, if any, the funding source will allow for indirect costs, and determine which portion of your budget the percentage applies to (epa 2010). It is important that the budget is compiled in close cooperation with staff from the financial department, so you would obtain realistic numbers. 00a budget format has usually three parts: (i) personnel costs, and (ii) non-personnel costs, (iii) indirect costs. Source: epa (2010) more tips for the development of your budget: it is important that the budget is realistic, as otherwise a donor will not take it serious. On the other hand, an underestimated budget might lead to a standstill or even a complete termination of activities in the midst of implementation (philip et al. Some donors require that some part of the cost of a project be borne by the applicant institution. Therefore, do not forget to list in-kind support and matching revenue, where s are prepared along with the development of a project proposal; therefore they are applicable in every project ping the budget is an excellent test of how clearly and completely the project has been described (university of idaho 2010)to organise your budget according to the commonly used categories would save you time and efforts when applying to different funding programmesthe budget provides a means to monitor the project’s financial activities over the life of the projecta budget provides a framework for expenditure to achieve the objectives of the project in an efficient mannercareful resource planning will decrease the number of changes of the budget during the lifetime of the project. Also, careful planning shows preparation of budgets costs time and money, and only in specific cases the project idea will fit a call of proposalsas a budget is an estimation of the project expenses, it is never accurate, and therefore it can bring problems during the implementation phasepoor financial planning can lead to budget constraints in the midst of operations and even complete terminationunrealistic budget planning causes failure to gain political (editor); u. The dsts have been developed by international organisations for planning and budgeting interventions in low income settings. This business model is designed to ensure affordable but high-quality services for consumers, profitability for the operators, and sufficient revenues for sustainable asset (editor) (2001): project cycle management technical guide.

Guide contains useful sections on project identification, design, appraisal and also proposal sity of virginia (editor) (2010): budget preparation. The manual also provides an introduction to finance policies and procedures, role of key officers in financing and accounting functions, how to budget and dealing with various financial transactions. Tools introductionfinancingfind funding options to implement your project here:financing and sources of fundingexecuting a projectafter the concept of your project is worked out, the budget is clear and the financing saved, your project can finally be executed:project implementationproject management.
