Statistical analysis in quantitative research
Us commence our look at data analysis g at a hypothetical research er that there are of approaching a research question and how we put together our research question will determine the methodology, data collection method, statistics, analysis and we will use to approach our research e of research females more likely to be nurses the proportion of males who are same as the proportion of females? There a relationship between gender the example in the box above, you can see are three different ways of approaching the research problem, which ned with the relationship between males and females in r research problem with another research problem - the n gender and smoking, there are 2 les (gender & smoker), with two or more categories in each, for example:You are looking for whether or not there is icance in the we proceed, you may want y refresh your knowledge and understanding of some basics, namely:Controlled double-blind tics, read chapter 9 of the accompanying book, and/or click on level (p level). Are just a few of the more common ones may come across in research test is used to test for n 2 independent groups on a continuous measure, e. Actually compares converts the scores on the the two then evaluates whether the medians two groups differ an rank test is used to demonstrate onship between two ranked ntly used to compare judgements by of judges on two objects, or the scores of a group of subjects is a shows the association between les (x and y), which are not normally about the details just remember is an acceptable method for parametric data when there are less than more than 9 paired test is used to compare the more than two samples, when either the data l or the distribution is not there are only two groups then it is lent of the mann-whitney u-test, so you may as well use test would normally be used when to determine the significance of difference among three or more is a very brief look at - for more information on statistical tests, read chapter 9 of common statistical. Is one of a number of tests (ancova - analysis ance - and manova - multivariate analysis of variance) that to describe/compare the relationship among a number of are two different types of chi-square tests - involve categorical data (pallant 2001). Type of chi-square test compares the frequency what is expected in theory against what is actually second type of chi-square test is known as -square test with two variables or the chi-square test is the most common nonparametric test for -sampled repeated measures design of research study, and is as the wilcoxon matched-pairs a very brief look at some of the more common statistical tests for is of data obtained from quantitative research - more details are given r 9 of the accompanying book.

Statistical analysis methods in research
There are, of course, many others, and statistics book will have details of the selection of the appropriate test for your research in order to p-value, you need to base the selection of four major factors,Level of data (nominal, ordinal, ratio, or interval). All these statistical tests may look cated, but if ever you are involved in quantitative research and have statistical analysis, don't worry because help is at is a computer package for is known as one of a number of computer packages that can do just calculation that you want, using any statistical we finish this section, we just need to remind be careful when you are looking at research that uses tions of /data/statistical look for these . Researchers should reflect on their study and discuss anything that did it perfect, for example:It is easy to tie yourself up into knots doing statistics as part of your research, or when reading , so remember two things:1. Statistics by themselves are meaningless, sion of statistics which makes them meaningful time has come for you which statistical test you will be using for your own ch. As we keep mentioning, if all this is new to you, do not hesitate the advice of an experienced quantitative researcher and/or a statistician. At as early a stage as on to the icon the example of a quantitative research study proposal:When you are satisfied have the correct statistical test(s), and you can justify it/them, ncbi web site requires javascript to tionresourceshow toabout ncbi accesskeysmy ncbisign in to ncbisign l listindian j anaesthv.
- evidence based interventions for childhood obesity
- disaster preparedness plan for business
- writing papers for students
Statistical analysis in qualitative research
Pmc5037948basic statistical tools in research and data analysiszulfiqar ali and s bala bhaskar1department of anaesthesiology, division of neuroanaesthesiology, sheri kashmir institute of medical sciences, soura, srinagar, jammu and kashmir, india1department of anaesthesiology and critical care, vijayanagar institute of medical sciences, bellary, karnataka, indiaaddress for correspondence: dr. 2016 october; 60(10): article has been cited by other articles in ctstatistical methods involved in carrying out a study include planning, designing, collecting data, analysing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of the research findings. The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. This article will try to acquaint the reader with the basic research tools that are utilised while conducting various studies. The article covers a brief outline of the variables, an understanding of quantitative and qualitative variables and the measures of central tendency. An idea of the sample size estimation, power analysis and the statistical errors is given.

Statistical methods in medical research
Finally, there is a summary of parametric and non-parametric tests used for data words: basic statistical tools, degree of dispersion, measures of central tendency, parametric tests and non-parametric tests, variables, varianceintroductionstatistics is a branch of science that deals with the collection, organisation, analysis of data and drawing of inferences from the samples to the whole population. 1] this requires a proper design of the study, an appropriate selection of the study sample and choice of a suitable statistical test. 3] variables such as height and weight are measured by some type of scale, convey quantitative information and are called as quantitative variables. With the fahrenheit scale, the difference between 70° and 75° is equal to the difference between 80° and 85°: the units of measurement are equal throughout the full range of the scales are similar to interval scales, in that equal differences between scale values have equal quantitative meaning. The p value is a numerical between 0 and 1 and is interpreted by researchers in deciding whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis [table 3]. 12]table 4illustration for null hypothesisparametric and non-parametric tests numerical data (quantitative variables) that are normally distributed are analysed with parametric tests.

13]two most basic prerequisites for parametric statistical analysis are:The assumption of normality which specifies that the means of the sample group are normally distributedthe assumption of equal variance which specifies that the variances of the samples and of their corresponding population are r, if the distribution of the sample is skewed towards one side or the distribution is unknown due to the small sample size, non-parametric[14] statistical techniques are used. Non-parametric tests are used to analyse ordinal and categorical tric tests the parametric tests assume that the data are on a quantitative (numerical) scale, with a normal distribution of the underlying population. The commonly used parametric tests are the student's t-test, analysis of variance (anova) and repeated measures t's t-teststudent's t-test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of the two groups. Simplified formula for the f statistic is:where msb is the mean squares between the groups and msw is the mean squares within ed measures analysis of varianceas with anova, repeated measures anova analyses the equality of means of three or more groups. The types of non-parametric analysis techniques and the corresponding parametric analysis techniques are delineated in table 5analogue of parametric and non-parametric testsmedian test for one sample: the sign test and wilcoxon's signed rank testthe sign test and wilcoxon's signed rank test are used for median tests of one sample. Therefore, it is useful when it is difficult to measure the on's signed rank testthere is a major limitation of sign test as we lose the quantitative information of the given data and merely use the + or – signs.

Wilcoxon's signed rank test not only examines the observed values in comparison with θ0 but also takes into consideration the relative sizes, adding more statistical power to the test. The data values are ranked in an increasing order, and the rank sums calculated followed by calculation of the test eere testin contrast to kruskal–wallis test, in jonckheere test, there is an a priori ordering that gives it a more statistical power than the kruskal–wallis test. If the outcome variable is dichotomous, then logistic regression is res available for statistics, sample size calculation and power analysisnumerous statistical software systems are available currently. The commonly used software systems are statistical package for the social sciences (spss – manufactured by ibm corporation), statistical analysis system ((sas – developed by sas institute north carolina, united states of america), r (designed by ross ihaka and robert gentleman from r core team), minitab (developed by minitab inc), stata (developed by statacorp) and the ms excel (developed by microsoft). A few are:Summaryit is important that a researcher knows the concepts of the basic statistical methods used for conduct of a research study. Inappropriate use of statistical techniques may lead to faulty conclusions, inducing errors and undermining the significance of the article.

Bad statistics may lead to bad research, and bad research may lead to unethical practice. Hence, an adequate knowledge of statistics and the appropriate use of statistical tests are important. An appropriate knowledge about the basic statistical methods will go a long way in improving the research designs and producing quality medical research which can be utilised for formulating the evidence-based ial support and cts of interestthere are no conflicts of nces1. Pmc free article] [pubmed]articles from indian journal of anaesthesia are provided here courtesy of wolters kluwer -- medknow s:article | pubreader | epub (beta) | printer friendly | pell institute and pathways to college , organize, & clean unit of e quantitative e qualitative ces & icate & e quantitative tative data analysis is helpful in evaluation because it provides quantifiable and easy to understand results. In this section, you will learn about the most common quantitative analysis procedures that are used in small program evaluation. You will also be provided with a list of helpful resources that will assist you in your own evaluative tative analysis in you begin your analysis, you must identify the level of measurement associated with the quantitative data.

You have identified your levels of measurement, you can begin using some of the quantitative data analysis procedures outlined below. Due to sample size restrictions, the types of quantitative methods at your disposal are limited. Correlation is a statistical calculation which describes the nature of the relationship between two variables (i. A correlation merely indicates that a relationship or pattern exists, but it does not mean that one variable is the cause of the example, you might see a strong positive correlation between participation in the summer program and students’ grades the following school year; however, the correlation will not tell you if the summer program is the reason why students’ grades were analysis of variance (anova) is used to determine whether the difference in means (averages) for two groups is statistically example, an analysis of variance will help you determine if the high school grades of those students who participated in the summer program are significantly different from the grades of students who did not participate in the sion is an extension of correlation and is used to determine whether one variable is a predictor of another variable. 2017 the pell institute for the study of opportunity in higher education, the institute for higher education policy, and pathways to college ctive learning evaluation ntly asked is data analysis? Of variables - of variables - is of quantitative is of quantitative data - standard of statistical ng a statistical tical test tics in research of statistical of statistical that you have looked at the distribution of your data and perhaps conducted some descriptive statistics to find out the mean, median, or mode, it is time to make some inferences about the data.

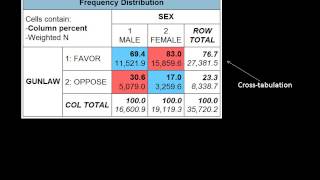
As previously covered in the module, inferential statistics are the set of statistical tests we use to make inferences about data. These statistical tests allow us to make inferences because they can tell us if the pattern we are observing is real or just due to do you know what kind of test to use? The decision of which statistical test to use depends on the research design, the distribution of the data, and the type of variable. Below is a table listing just a few common statistical tests and their tests look for an association between for the strength of the association between two continuous for the strength of the association between two ordinal variables (does not rely on the assumption of normally distributed data). For the strength of the association between two categorical ison of means: look for the difference between the means of for the difference between two related for the difference between two independent the difference between group means after any other variance in the outcome variable is accounted sion: assess if change in one variable predicts change in another how change in the predictor variable predicts the level of change in the outcome how change in the combination of two or more predictor variables predict the level of change in the outcome -parametric: used when the data does not meet assumptions required for parametric on rank-sum for the difference between two independent variables—takes into account magnitude and direction of on sign-rank for the difference between two related variables—takes into account the magnitude and direction of if two related variables are different—ignores the magnitude of change, only takes into account this link for a printable pdf version of this table: common statistical ng a statistical hare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. It is made for research methodology you sure you want message goes viviana carvalho in marketing and digital media, escp come in the pie within the "distribution (cont)" slide, the percentages are different than in the table ?
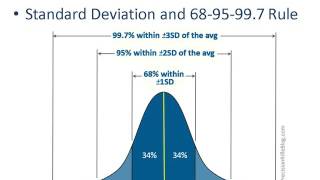
You sure you want message goes ant manager at kkm , univariate analysis subgroup comparisons focus on describing the people (or other unit of analysis) under study, whereas bivariate analysis focuses on the variables and empirical tative data analysis. Quantitative analysis involves the techniques researchers convert data to and subject them to statistical analyses. 5 likerttype scale into of variables iate analysis is is does not onships or more variables, e is more ptive rather ncy distribution is counts of the number se to a question or to the occurrence of enon of interest. Researcher some general picture about sion, as well as maximum and is your religious preference? Marijuana legalization by age of respondents, not be : general social survey, 2004, national opinion research up comparisons tell how different groups this question and some pattern in the results. Finally, the table is read by independent variable one another in terms of a ute of the dependent ariate analysis of the simultaneous relationships among.
The effects of religious attendance, gender, and be and example of multivariate ariate relationship: religious attendance, gender, and : general social survey, 1972 – 2006, national opinion research ogical ogical diagnostics is a quantitative analysis determining the nature of social problems such or gender discrimination. Can be used to replace opinions with facts and to s with data of gender and e family pattern, women as group ipated less in in the labor force and many only e the home after completing certain quantitative data analysis we classify features, , and even construct more complex statistical an attempt to explain what is gs can be generalized to a larger population, comparisons can be made between two corpora, as valid sampling and significance techniques , quantitative analysis allows us to discover ena are likely to be genuine reflections of or of a language or variety, and which are ment committee. Course - linkedin ic research foundations: course - linkedin ng techniques: creating effective learning course - linkedin ative data n nigatu ng methods in qualitative and quantitative ative data analysis ative data analysis (steps).
