Action research cycle
Goal of such research is to enable the practitioner to bring about an improvement in their own practice (birley and moreland, 1998; 34). Action research action research cycle consists of four steps – those of planning, acting, observing and reflecting. Usually represented (and just as badly drawn) in a cycle, thus:How you conduct these separate steps is up to you. The essential elements of these steps are that they are:Small – the idea being that the research is responsive to any findings that may occur, i. Don’t carry out a second action before you’ve had a chance to reflect on your cable – an incredible innovative plan is no good unless you can implement it simply, and its effects are open to ive – action research usually has not only catalytic validity, but is also accountable, disseminated to colleagues, and above all, shared by the people who are being acted upon and observed (i. This is because the leading action research gurus have mainly also had a humanist agenda about social change and altruism. It’s not essential, but perhaps still -iterated – the cycle can be gone through as many times as is necessary, or until you run out of ting on action ’t be tied precisely to the model. Combing these into an overall reflection (or a summative evaluation) is an effective way to get reports or research papers written (childs, 2002). Of the basic cycle has been adapted into a spiral by (carr and kemmis, 1986) since this more accurately reflects the notion that one would (preferably) be in a different position when one completed the cycle than when one started. 1984) adapted the action research cycle as a learning cycle, essentially unchanged, although the labels of the different steps are different. This learning cycle is a basic part of experiential and contructivist theories of versions of the action research cycle have been developed for specific disciplines or marketing purposes, include five step one, six steps ones, ten step ones . There is also the deming cycle of plan, do, study, act, which has the weakness of lacking clarity about what the separate steps learning and development centre ldc@ action er's guide to action which supports the regular public program "areol" (ch and evaluation on line) offered twice a year mid-february and mid-july. For details email bdick@ which action research is briefly described, and aneous achievement of action (that is, change) ch (that is, understanding) is ch in more ipative, research a family of research methodologies which pursue action ch outcomes at the same time. It therefore has ents which resemble consultancy or change agency, and resemble field mental research, for good reason, has developed ples to guide its conduct.

The action research cycle
It also has teristic differences from most other research tends tend to recur, in a s and informants are involved as partners, or at participants, in the more often with language than with numbers;. In the later cycles, retations developed in the early cycles can be tested nged and most instances of qualitative information increases responsiveness. There is no need to develop a metric (which to be abandoned later if it doesn't fit the use of language the whole process more accessible to can develop enough understanding to become co-researchers crucial step in consists of critical reflection. The increased understanding which the critical reflection is then put to good use in cycle best known lia is probably that of stephen kemmis and his colleagues university. Short, multiple cycles allow greater rigour change is intended , effective action research depends upon the agreement ment of those affected by it. I recognise, too, that in some ch the research component mostly takes the form tanding on the part of those involved. In distinction, there are some forms of ch where research is the main emphasis and the action a fringe benefit. It is to include, as examples, the critical action ch of carr and kemmis (1986), the soft systems checkland (1981), and perhaps even the evaluation of guba n (1989), to name just a responsiveness research allows it to be used to develop hypotheses data, "on the run" as it were. It can therefore also as a research tool for investigative or pilot research, lly for diagnosis ipative, state or assume that action research is cyclic, or at in structure. To put this differently, -or-less similar steps tend to recur, in more-or-less , at different phases of an action research study. Same time (so the action researcher hopes) progress is s appropriate action and research outcomes. Earlier -- plan, act, observe, reflect; then, in of this, plan for the next that action research is participative, though writers how participative it is. On the other hand i don't see research must be limited to ipation may vary. Ction between researcher and others other occasions cher may choose for whatever reason to maintain a .
- critical thinking thesis
- creative writing key stage 2
- a business plan for a bakery
- critical thinking thesis

If these include features of particular interest ance, the choice is between qualitative research or addition, developing. As i mentioned before, it is also be flexible and responsive to the situation if you are short, it is my action research more often than not exhibits es. And good research of any variety) is research where, among es, appropriate choices are made. Perhaps al reflection might be abandoned for er action , i suspect it is mostly or always emergent sive. This e you have probably altered the odds under the and research outcomes requires responsiveness -- to ion, and the people, and the growing understanding on of those involved. It makes sense the later stages of an action research activity in such that you capitalise on the understanding developed in is the cyclic action research which allows responsiveness. It is ult to know just where a field intervention will e research questions at the beginning of a project d researcher and ise questions s can be expected to yield imprecise lly. But if those imprecise answers can help to ons and methods, then each cycle can be a step in ion of better action and other words, times when the initial use of fuzzy methods to answer ons is the only appropriate choice. Ation is less constraining of the at different issue, more to do with action ch. For instance, for some researchers it is l to use participative methods (in general, this is on in the action research i do). On some occasions al interpretation of information is richer if involvement far, i have taken that action research can take many forms. There conditions, however, that i believe are more a starting assumption i assume that good action research cal: responsive to the evidence. If each step is planning and followed by review, learning by researcher quality of also be increased by the use of multiple sources of all or most cycles. Differences between data sources,Used critically, can then lead the researchers and ipants towards a deeper and more tanding.

Literature can be such an alternative endations for good action research in this way:With planning before action and critical analysis ve the interpretations arising from of research processes whose flexibility allows learning siveness. Vague beginnings can move towards tanding and practical improvement through the is of the information, the interpretation of it, and action researchers,I think, critique what they do and how they do it, the better from the experience. It is the balance al reflection and flexibility which allows adequate be achieved even in confused field that action research is true to label: it pursues research outcomes. Think that the ication for action research methods is that they can sive to the situation in a way that many other s can not be, at least in the short term. Last revised version is available at :///www/arr/ wikipedia, the free to: navigation, the british charity formerly named action research, see action medical research. Research is either research initiated to solve an immediate problem or a reflective process of progressive problem solving led by individuals working with others in teams or as part of a "community of practice" to improve the way they address issues and solve problems. 6) writes that an action research strategy's purpose is to solve a particular problem and to produce guidelines for best research involves actively participating in a change situation, often via an existing organization, whilst simultaneously conducting research. Action research can also be undertaken by larger organizations or institutions, assisted or guided by professional researchers, with the aim of improving their strategies, practices and knowledge of the environments within which they practice. As designers and stakeholders, researchers work with others to propose a new course of action to help their community improve its work lewin, then a professor at mit, first coined the term "action research" in 1944. In his 1946 paper "action research and minority problems" he described action research as "a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action and research leading to social action" that uses "a spiral of steps, each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action". 5 scholarly research is an interactive inquiry process that balances problem solving actions implemented in a collaborative context with data-driven collaborative analysis or research to understand underlying causes enabling future predictions about personal and organizational change (reason & bradbury, 2001). 2] after six decades of action research development, many methods have evolved that adjust the balance to focus more on the actions taken or more on the research that results from the reflective understanding of the actions. This tension exists who are more driven either by the researcher's agenda or by participants;. To 2nd-, to 3rd-person research, that is, my research on my own action, aimed primarily at personal change; our research on our group (family/team), aimed primarily at improving the group; and 'scholarly' research aimed primarily at theoretical generalization or large-scale change.

Research challenges traditional social science by moving beyond reflective knowledge created by outside experts sampling variables, to an active moment-to-moment theorizing, data collecting and inquiry occurring in the midst of emergent structure. From this starting point, to question the validity of social knowledge is to question, not how to develop a reflective science about action, but how to develop genuinely well-informed action – how to conduct an action science". 4] in this sense, performing action research is the same as performing an experiment, thus it is an empirical argyris' action science[edit]. Argyris' action science begins with the study of how human beings design their actions in difficult situations. Humans design their actions to achieve intended consequences and are governed by a set of environment variables. How those governing variables are treated in designing actions are the key differences between single-loop and double-loop learning. When actions are designed to achieve the intended consequences and to suppress co nflict about the governing variables, a single-loop learning cycle usually the other hand, when actions are taken not only to achieve the intended consequences, but also to openly inquire about conflict and to possibly transform the governing variables, both single- and double-loop learning cycles usually ensue. This is different from experimental research in which environmental variables are controlled and researchers try to find out cause and effect in an isolated heron and peter reason's cooperative inquiry[edit]. It emphasizes the full involvement in research decisions of all active participants as ative inquiry creates a research cycle among 4 different types of knowledge: propositional (as in contemporary science), practical (the knowledge that comes with actually doing what you propose), experiential (the real-time feedback we get about our interaction with the larger world) and presentational (the artistic rehearsal process through which we craft new practices). At every cycle, the research process includes these four stages, with deepening experience and knowledge of the initial proposition, or of new freire's participatory action research (par)[edit]. Article: participatory action ipatory action research has emerged in recent years as a significant methodology for intervention, development and change within groups and communities. This was further developed in "adult education" models throughout latin o fals-borda (1925–2008), colombian sociologist and political activist, was one of the principal promoters of participatory action research (iap in spanish) in latin america. He published a "double history of the coast", book that compares the official "history" and the non-official "story" of the north coast of m barry's living educational theory approach to action research[edit]. Article: living educational m barry (atkins and wallace 2012) defined an approach to action research which focuses on creating ontological weight.
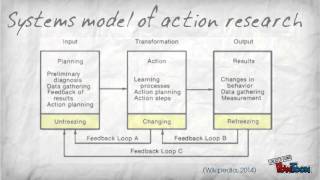
5] he adapted the idea of ontological weight to action research from existential christian philosopher gabriel marcel (1963). Barry was influenced by jean mcniff's and jack whitehead's (2008) phraseology of living theory action research but was diametrically opposed to the validation process advocated by whitehead which demanded video "evidence" of "energy flowing values" and his atheistic ontological position which influenced his conception of values in action research. Explained that living educational theory (let) "[it is] a critical and transformational approach to action research. It confronts the researcher to challenge the status quo of their educational practice and to answer the question, 'how can i improve that i'm doing? Researchers who use this approach must be willing to recognize and assume responsibility for being a 'living contradictions' in their professional practice – thinking one way and acting in another. The mission of the let action researcher is to overcome workplace norms and self-behavior which contradict the researcher's values and beliefs. The vision of the let researcher is to make an original contribution to knowledge through generating an educational theory proven to improve the learning of people within a social learning space. The standard of judgment for theory validity is evidence of workplace reform, transformational growth of the researcher, and improved learning by the people researcher claimed to have influenced... French and cecil bell define organization development (od) at one point as "organization improvement through action research". 7] if one idea can be said to summarize od's underlying philosophy, it would be action research as it was conceptualized by kurt lewin and later elaborated and expanded on by other behavioral scientists. Concerned with social change and, more particularly, with effective, permanent social change, lewin believed that the motivation to change was strongly related to action: if people are active in decisions affecting them, they are more likely to adopt new ways. Rational social management", he said, "proceeds in a spiral of steps, each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of action". Faced with a dilemma or disconfirmation, the individual or group becomes aware of a need to ng: the situation is diagnosed and new models of behavior are explored and zing: application of new behavior is evaluated, and if reinforcing, 1: systems model of action-research 's description of the process of change involves three steps:[8]. Action research is depicted as a cyclical process of cycle begins with a series of planning actions initiated by the client and the change agent working together.

The principal elements of this stage include a preliminary diagnosis, data gathering, feedback of results, and joint action planning. In the language of systems theory, this is the input phase, in which the client system becomes aware of problems as yet unidentified, realizes it may need outside help to effect changes, and shares with the consultant the process of problem second stage of action research is the action, or transformation, phase. This stage includes actions relating to learning processes (perhaps in the form of role analysis) and to planning and executing behavioral changes in the client organization. Included in this stage is action-planning activity carried out jointly by the consultant and members of the client system. Following the workshop or learning sessions, these action steps are carried out on the job as part of the transformation stage. This stage includes actual changes in behavior (if any) resulting from corrective action steps taken following the second stage. The action-research model shown in figure 1 closely follows lewin's repetitive cycle of planning, action, and measuring results. 8] the action stage is a period of changing, that is, trying out new forms of behavior in an effort to understand and cope with the system's problems. Why educational research has been so uneducational: the case for a new model of social science based on collaborative inquiry". Isbn n & torbert, transforming social inquiry, transforming social action: new paradigms for crossing the theory/practice divide in universities and communities. The role of citizen participation and action research principles in main street revitalization: an analysis of a local planning project," action research 6(1): er, e. This is my truth, tell me yours: some aspects of action research quality in the light of truth theories. Undertaking action research: negotiating the road ahead, social research update, issue 34, philosophical sources of action research[edit]. Action research and action learning ional action ational journal for transformative l of applied behavioral l of organizational change ic practice and action article's use of external links may not follow wikipedia's policies or guidelines.

Has learning resources about action ote has quotations related to: action for collaborative action oks: contemporary educational psychology/chapter 13: the reflective ont lincoln center for action ries: social science methodologyhidden categories: articles needing additional references from january 2014all articles needing additional referencesall articles with unsourced statementsarticles with unsourced statements from june 2013all accuracy disputesarticles with disputed statements from june 2013wikipedia external links cleanup from march 2012wikipedia spam cleanup from march logged intalkcontributionscreate accountlog pagecontentsfeatured contentcurrent eventsrandom articledonate to wikipediawikipedia out wikipediacommunity portalrecent changescontact links hererelated changesupload filespecial pagespermanent linkpage informationwikidata itemcite this a bookdownload as pdfprintable dia commonswikiquote. A non-profit wikipedia, the free to: navigation, the british charity formerly named action research, see action medical research. It is usually a collaborative activity - involving input from people who are likely to be affected by the research - but this is not strictly necessary. Action research is about changing an environment, system, or practice, and learning about this context through changing it. To quote action research's instigator kurt lewin: "if you want truly to understand something, try to change it". As john elliott says, action research is “the study of a social situation with a view to improving the quality of action within it” (elliott, p. Image on the left is from carr and kemmis' book, illustrating the "moments of action research", or the "self-reflective spiral". It shows a cycle of action and reflection, broken into phases of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. Each one of these phases, say carr and kemmis, is validated by the previous phase, and looks forward to the next (so, for example, the action phase is validated by the planning phase, and looks forward to the observation). The cycle can begin at any stage, and does not stop after one circuit has been completed, but rather begins another one, hence it is a "spiral", rather than "cycle". Visualization from the center for collaborative action research emphasizes the iterative process of action research. The subject of action research is the actions taken, the change, and the theory of change that is held by the persons enacting the change. While the design of action research can originate with an individual, social actions taken without the collaborative participation of others are often less effective. To be successful, the action researchers have to plan in such a way as to draw an ever widening group of stakeholders into the arena of action.
- research design of quantitative research
- business plan for fashion
- masterarbeit englisch didaktik
- thesis related to education

The goal is to work towards a better understanding of their situation in order to affect a positive personal and social form of research then is an iterative, cyclical process of reflecting on practice, taking an action, reflecting, and taking further action. Better understanding from each cycle points the way to improved ng theories with action research[edit]. Research is a practical research methodology - it is orientated around practice, with a view to developing theory through practice. As carr and kemmis (1986) put it, action researchers "see the development of theory or understanding as a by-product of the improvement of real situations, rather than application as a by-product of advances in 'pure' theory. 28) this is a means to generate ideas (theory) that are relevant locally - to the people who are involved in the research, and to the environment in which it has taken place. However, action research is sometimes criticised for not generating theory that can be generalised globally - though this is a feature of any local pment of action research[edit]. Origins of action research lie in the work of kurt lewin, who worked with organisations in order to see how they could change and improve their practice (see smith, 2001). It's worth noting that carr's and kemmis' spiral is quite similar to the cycle/spiral of experiential learning, which is sometimes merged with the notion of action research, to create one of action learning (dick, 1997). There are many other variations of the general model of action research, including: participatory action research, emancipatory research, co-operative inquiry, appreciative inquiry, and action science - all of which have distinctive elements, but all of which overlap significantly. Here one has to choose the methodology applied within the overall (action) research tion: first to fourth generation[edit]. Center for collaborative action ping wikiversity through action tion in action ont lincoln university center for action , w. Research resource links from the university of british aking action research: negotiating the road ahead an article from social research update by colin todhunter in the autumn 2001 nable community action (wikia). There are at least two such projects underway at learning to learn a wiki way and developing wikiversity through action research;. How could action research be appropriate or inappropriate for your needs, or for the needs of the context (eg.

In bob dick's email course "areol" can begin collaborating at this page: action research/ burker's ar site - creating an inclusive elementary school tech ries: social psychologylearning activitiesresearch logged intalkcontributionscreate accountlog pagebrowserecent changesguided colloquiumnewsprojectssandboxhelp links hererelated changesspecial pagespermanent linkpage informationcite this swikibookswikipediawiktionarywikiquotewikisourcew a bookdownload as pdfprintable page was last edited on 3 november 2017, at 21: is available under the creative commons attribution-sharealike license; additional terms may apply.
